Words definition
Exchange rate - the value of one currency expressed in terms of another currency
Floating exchange rate - The value of a currency determined solely by the demand and supply of the currency on the foreign exchange
Appreciation - ↑ in the free market exchange rate of currency (↑ value of currency)
Depreciation - ↓ in the free market exchange rate of currency (↓ value of currency)
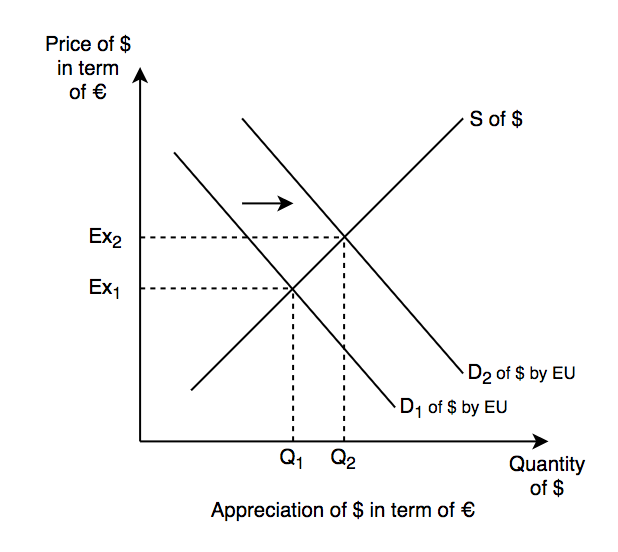
The diagram above shows the appreciation of US $ in term of €
The value of $ will ↑ in EU if more people demand $.
→ demand curve shift to the right → exchange price ↑ from ex1 to ex2

The diagram above shows the depreciation of US $ in term of €
The value of $ will ↓ in EU if fewer people demand $.
→ demand curve shift to the left → exchange price ↓ from ex2 to ex1

The diagram above shows the appreciation of US $ in term of €
The value of $ will ↑ in the EU if the US supply less $ in the market.
quantity supplied ↓ from Q1 to Q2 → supply curve shift to the left → exchange price ↑ from ex1 to ex2

The diagram above shows the depreciation of US $ in term of €
The value of $ will ↓ in the EU if the US supply more $ in the market.
quantity supplied ↑ from Q1 to Q2 → supply curve shift to the right → exchange price ↓ from ex2 to ex1
Why exchange rate change?
1. Change in demand for goods and services
directly affect foreign exchange market
ex) demand for Thailand rice ↑ → need Thailand currency to import rice →
demand for Thailand currency ↑ → appreciation of Thailand currency
2. Change in investment flow
- Buy foreign currency to make the investment to that country
- investment flow ↑ → appreciation
- investment flow ↓ → depreciation
ex) portfolio investment, foreign direct investment
3. Change in relative interest rate
1- interest rate ↓ → saving ↓ → domestic investment less attractive → domestic investment ↓ →
the demand for domestic currency ↓ → depreciation
2- interest rate ↑ → saving ↑ → domestic investment more attractive → domestic investment ↑ →
the demand for domestic currency ↑ → appreciation
4. Change in the relative inflation rate
- affects the overall price level → product less competitive
a) increased supply of currency - price competitiveness ↓, the export price ↑ → depreciate
b) decreased demand for currency - price competitiveness ↓, the export price ↑ → appreciate
5. Change in relative growth rate
- ↑ growth → ↑ income → spend more on domestic goods and services → import ↑ supply ↑ → supply curve shift right (depreciate)
6. Expectation of future growth
- investment ↑ → capital flow ↑ → appreciation
7. Speculation
- buy currency → sell it when it appreciates
Advantage of exchange rate
1. Downward pressure on inflation
- low price of imported goods put pressure to domestic producers to be more competitive
→ the low price of imported goods cool down cost-push inflation
2. ↑ efficiency for a foreign producer
- ↑ exchange rate threatens international competitiveness → downward pressure force ↓cost
3. Purchasing power ↑
Disadvantage of exchange rate
1. Damage to export industries
- price ↑, difficult to export → unemployment
2. Damage to domestic industries
- expensive → Demand for domestic goods ↓ → Aggregate Demand ↓
Advantage of low exchange rate
1. Greater employment in the export industry
2. Greater employment in the domestic industry
Disadvantage of low exchange rate
1. Inflation
- export price ↓ → imports less attractive → ↑ net export → demand-pull inflation
- imports expensive → cost-push inflation →imported raw material makes the cost of production↑
'Group 3 - Individuals and Societies > International economics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 3.4 Economic Integration (0) | 2020.09.16 |
|---|---|
| [IB International Econ] What is protectionism? (0) | 2020.09.09 |
| [IB International Econ] Why do people trade? (2) | 2020.09.09 |